BIOSENSORS
checks the quality of air & water, and toxicity levels of wastewater.
are used in detecting pathogens in fresh meat, poultry or fish.
are used to monitor blood glucose levels in diabetes patients.
What are biosensors?
Biosensors or "biological sensors" are devices made up of a transducer and a bioreceptor which can identify analytes and turn that information into a measurable signal.
Click on the video above to learn more about the meaning behind biosensors, its uses, and how biosensors work.
The Main Types of Biosensors

How Technological Biosensors Work
1
The analyte, or biological element, is placed in the biosensor, then that specific molecule will be distinguished from any others.
2
The bioreceptor is a biomolecule that recognizes the analyte. This is where the recognition event takes place.
3
The transducer turns the recognition occurrence into a measurable signal.
4
5
6
The amplifier heightens the intensity of the signal.
The processor further intensifies and separate out unwanted noises for the signal to be read easier.
The display shows the data and results from the processor onto a screen.
Did You Know Biosensors...



Advantages
Disadvantages
specific because of a system particular to biosensors
can achieve rapid and continuous control
response times are short (usually <1min)
practical to use
heat sterilization isn't possible due to denaturaziation of analyte
can be tampered with by pH, temperature, or ions
usually low cost and simple to make
minimal and accurate
the cells in the biosensor can become intoxicated by other molecules that diffuse through the membrane
What Impact Does Biosensors Have on the World?

Take the worldwide spread of diabetes as an example. As stated above, every year about 5 million people die due to diabetes related causes. However, this number would be substantially larger if not for the use of biosensors, specifically blood glucose monitors.
Blood glucose monitors, which are examples of biosensors, help calculate blood glucose levels, alerting the user if their blood glucose levels are too low. Without this small, but necessary device, mortality rates would be much greater, as the side effects of having low blood glucose levels can lead to death.
certain biosensors have to be operated by professionals
Cost of Biosensor: Looking Into the Value of the Biosensor Industry
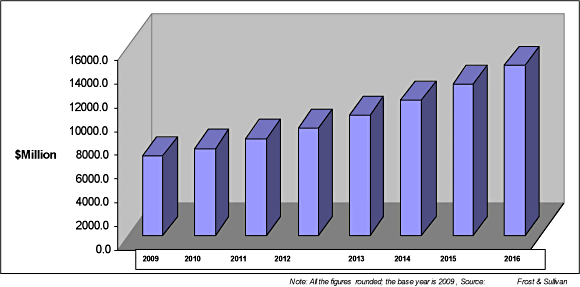
The bar graph above depicts the amount of revenue (in millions) throughout the years. In 2016, the amount of revenue was a little under $16,000 million, while the revenue in 2009 was about $8,000 million, showing about a double revenue amount increase. This drastic change in the amount of revenue over 7 years shows that the biosensor industry is constantly expanding and growing.
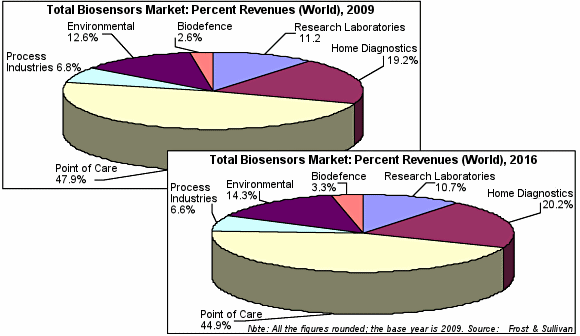
To the left is a pie chart depicting in percentage of the world revenue in the different biosensor applications. As can be seen, point of care held the highest percent revenue, with over 44% in both 2009 and 2016. A point of care device can be a hospital-use blood glucose monitor, with the intention of patient use. The second leading application is home diagnostics at about 19.7% between 2009 and 2016. Home diagnostic devices are innovations such as the home glucose monitors for diabetes, or a standard thermometer.
Different Types of Biosensors
There are 6 main biosensors, and they're mainly classified based on two parts: the bio-recognition element and the transducer. The bio-recognition element detects the analyte, and the transducer translates the physical change into energy.

Again, as can be seen on the chart to the left, bioreceptors (bio-recognition elements) and transducers determine what kind of biosensors there are. The bioreceptors are not limited to those four, and can also include tissues and microorganisms. Also, the other main transducers are ion-sensitive and resonant.
So...What Are the Different Types of Biosensors?
*Click On the Images Above to Learn More